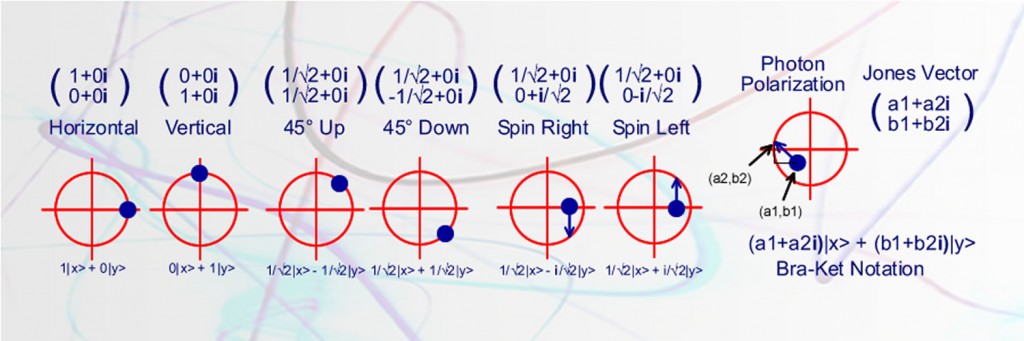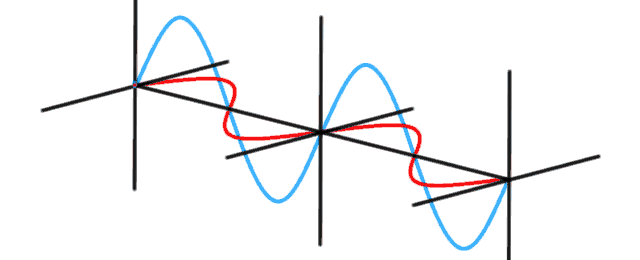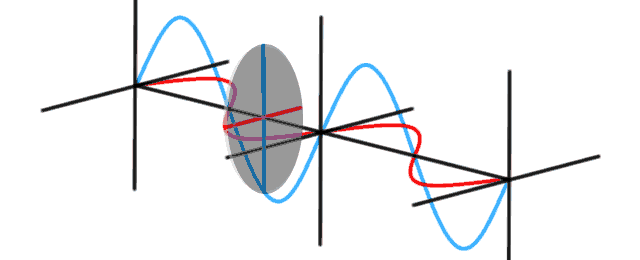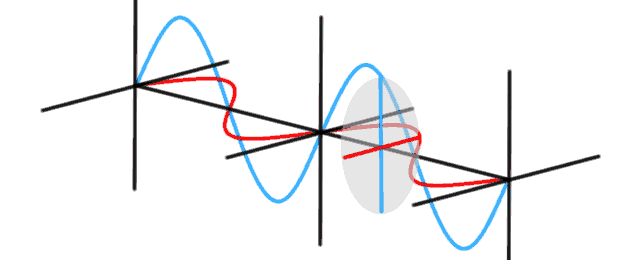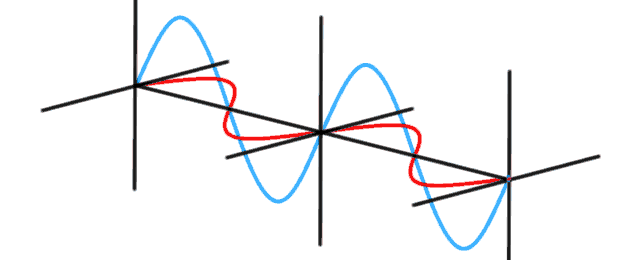
Modelling a photon presents a number of challenges. In quantum physics, a photon flies through the air like a wave. They diffract around corners like a wave. Photons interact with each other like waves. Sometimes they reinforce each other, sometimes they interfere and seem to disappear. The classical explanation uses Maxwell’s equations to describe the wave nature of light. Light waves […]